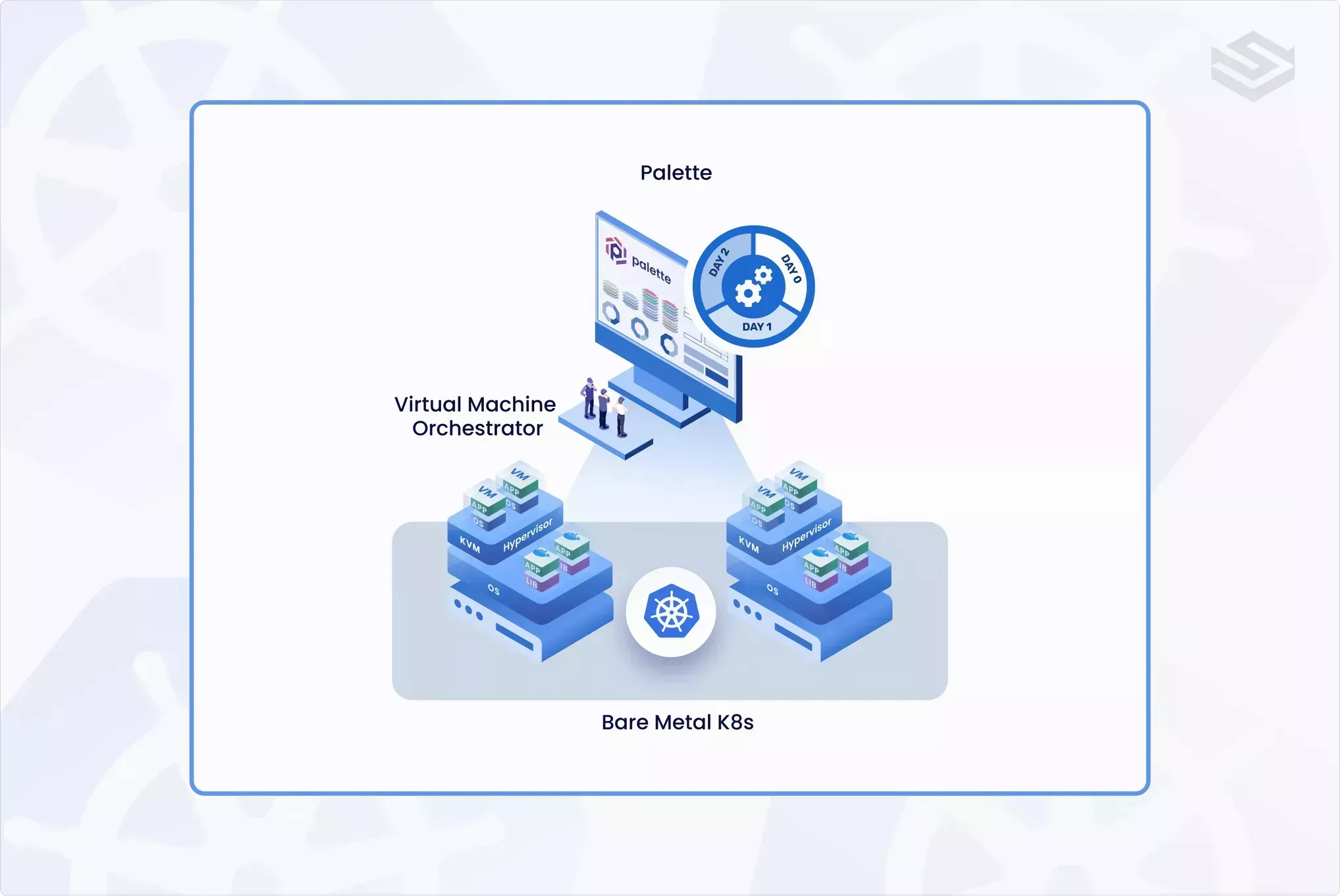
Virtual Machine Orchestrator
Palette Virtual Machine Orchestrator (VMO) provides a unified platform for managing containerized and virtualized applications. This solution allows organizations to onboard, deploy, manage, and scale VMs within the same cluster as their containerized applications. Palette VM Orchestrator simplifies managing infrastructure, improves resource utilization, and removes the cost of having a hypervisor.
Use Cases
Palette VM Orchestrator is particularly suitable in the following scenarios:
-
Organizations that want to remove their virtualization infrastructure due to an aging environment or to reduce costs. By using Palette VM Orchestrator, legacy applications and modern, containerized applications can be deployed on VMs.
-
Edge locations with a few VMs deployed and where a hypervisor is no longer desired.
Prerequisites
Palette Virtual Machine Orchestrator requires the following:
-
Palette version 3.3.0 or higher.
-
For data centers, production VMs are supported on bare metal Kubernetes clusters deployed on Canonical MAAS. To learn how to configure MAAS and create MAAS clusters in Palette, refer to the Deploy to MAAS guide.
-
For Edge deployment, your Edge cluster profile must have a CSI pack. For more information, refer to Create VMO Profile in the Edge tab.
-
VMs with Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) must have a StorageClass that supports
ReadWriteMany(RWX) access mode for seamless live migration to a different node - either when triggered manually or during a Kubernetes upgrades.warningIn environments that use nested virtualization, where VMs operate inside of VMs due to lack of hardware to host VMs, it is technically possible to operate VMs in Kubernetes by setting the KubeVirt resource
useEmulationto true. However, we do not recommend this approach.
Get Started With VM Orchestrator
To get started, review Virtual Machine Orchestrator Pack to learn about its components.
Review Create a VMO Profile and Add Roles and Role Bindings to learn how to create the cluster profile and add roles and permissions that allow users to create and manage Virtual Machines (VMs).
Palette VM Orchestrator provides various methods to quickly deploy VMs from out-of-the-box templates or from your organization's templates. To learn more about using and creating templates, review Deploy VM From a Template and Create a VM Template.
While you can import template disks from external locations when deploying a VM, it can be inefficient. Instead, you can
leverage the DataVolume resource to import template disks once and then clone them when deploying new VMs. Review the
Create Disk Templates guide for more information.
Feature Gates
Palette VM Orchestrator utilizes open-source KubeVirt as a component of the Virtual Machine Orchestrator pack to manage VMs and enables the following KubeVirt feature gates by default:
- LiveMigration
- Snapshot
- HotplugVolumes
- VMExport
- ExpandDisks
- HotplugNICs
- VMLiveUpdateFeatures
KubeVirt offers other feature gates you may find useful and which you can enable using
Kubernetes feature gates. To enable
more KubeVirt feature gates, you can modify the kubevirt.kubevirtResource.additonalFeatureGates parameter in the
Virtual Machine Orchestrator manifest.
For more information on KubeVirt feature gates, refer to the KubeVirt user guide.
Kubevirt Plugins
VMO includes the following KubeVirt plugins:
- Kubevirt-Velero - VMO includes the Kubevirt-Velero plugin, which allows you to back up and restore VMs using Velero. This installs Velero snapshot controller and Custom Resource Definitions required by Velero. Refer to the Virtual Machine Orchestrator Pack guide for more information.